Electrochem Seminar - 'Quantitative Decoupling of Oxygen-Redox and Manganese-Redox Voltage Hysteresis in a Cation-Disordered Rock Salt Cathode' - Tzu-Yang Huang
Electrochem Seminar - 'Quantitative Decoupling of Oxygen-Redox and Manganese-Redox Voltage Hysteresis in a Cation-Disordered Rock Salt Cathode' - Tzu-Yang Huang
Abstract
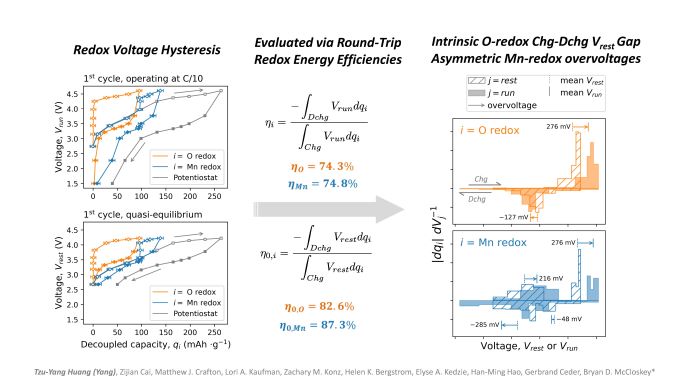
Pronounced voltage hysteresis is commonly thought to be associated with oxygen redox in Li-excess cathode materials. However, they often possess overlapping oxygen and transition-metal redox, whose contributions to voltage hysteresis are challenging to distinguish. In this talk, the development of a two-step aqueous redox titration with the aid of mass spectrometry (MS) will be introduced to quantify oxidized lattice oxygen and Mn3+/4+ redox in a representative Li-excess cation-disordered rock salt –– Li1.2Mn0.4Ti0.4O2 (LMTO). Two MS-countable gas molecules evolve from two separate titrant-analyte reactions, thereby allowing Mn and O redox capacities to be decoupled. The decoupled O and Mn redox coulombic efficiencies are close to 100% for the LMTO cathode, indicating high charge-compensation reversibility. As incremental capacities are quantitatively decoupled, each redox voltage hysteresis is further evaluated. Overall, LMTO voltage hysteresis arises not only from an intrinsic charge-discharge voltage mismatch related to O redox, but also from asymmetric Mn-redox overvoltages. The results reveal that O and Mn redox both contribute substantially to voltage hysteresis. This work further shows the potential of designing new analytical workflows to experimentally quantify key properties, even in a disordered material having complex local coordination environments.
Speaker
Tzu-Yu Huang